Develop a serverless application in Python using Amazon CodeWhisperer
January 23, 2023While writing code to develop applications, developers must keep up with multiple programming languages, frameworks, software libraries, and popular cloud services from providers such as AWS. Even though developers can find code snippets on developer communities, to either learn from them or repurpose the code, manually searching for the snippets with an exact or even similar use case is a distracting and time-consuming process. They have to do all of this while making sure that they’re following the correct programming syntax and best coding practices.
Amazon CodeWhisperer, a machine learning (ML) powered coding aide for developers, lets you overcome those challenges. Developers can simply write a comment that outlines a specific task in plain English, such as “upload a file to S3.” Based on this, CodeWhisperer automatically determines which cloud services and public libraries are best-suited for the specified task, it creates the specific code on the fly, and then it recommends the generated code snippets directly in the IDE. And this isn’t about copy-pasting code from the web, but generating code based on the context of your file, such as which libraries and versions you have, as well as the existing code. Moreover, CodeWhisperer seamlessly integrates with your Visual Studio Code and JetBrains IDEs so that you can stay focused and never leave the development environment. At the time of this writing, CodeWhisperer supports Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, and TypeScript.
In this post, we’ll build a full-fledged, event-driven, serverless application for image recognition. With the aid of CodeWhisperer, you’ll write your own code that runs on top of AWS Lambda to interact with Amazon Rekognition, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS), Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS), Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), and third-party HTTP APIs to perform image recognition. The users of the application can interact with it by either sending the URL of an image for processing, or by listing the images and the objects present on each image.
Solution overview
To make our application easier to digest, we’ll split it into three segments:
- Image download – The user provides an image URL to the first API. A Lambda function downloads the image from the URL and stores it on an S3 bucket. Amazon S3 automatically sends a notification to an Amazon SNS topic informing that a new image is ready for processing. Amazon SNS then delivers the message to an Amazon SQS queue.
- Image recognition – A second Lambda function handles the orchestration and processing of the image. It receives the message from the Amazon SQS queue, sends the image for Amazon Rekognition to process, stores the recognition results on a DynamoDB table, and sends a message with those results as JSON to a second Amazon SNS topic used in section three. A user can list the images and the objects present on each image by calling a second API which queries the DynamoDB table.
- 3rd-party integration – The last Lambda function reads the message from the second Amazon SQS queue. At this point, the Lambda function must deliver that message to a fictitious external e-mail server HTTP API that supports only XML payloads. Because of that, the Lambda function converts the JSON message to XML. Lastly, the function sends the XML object via HTTP POST to the e-mail server.
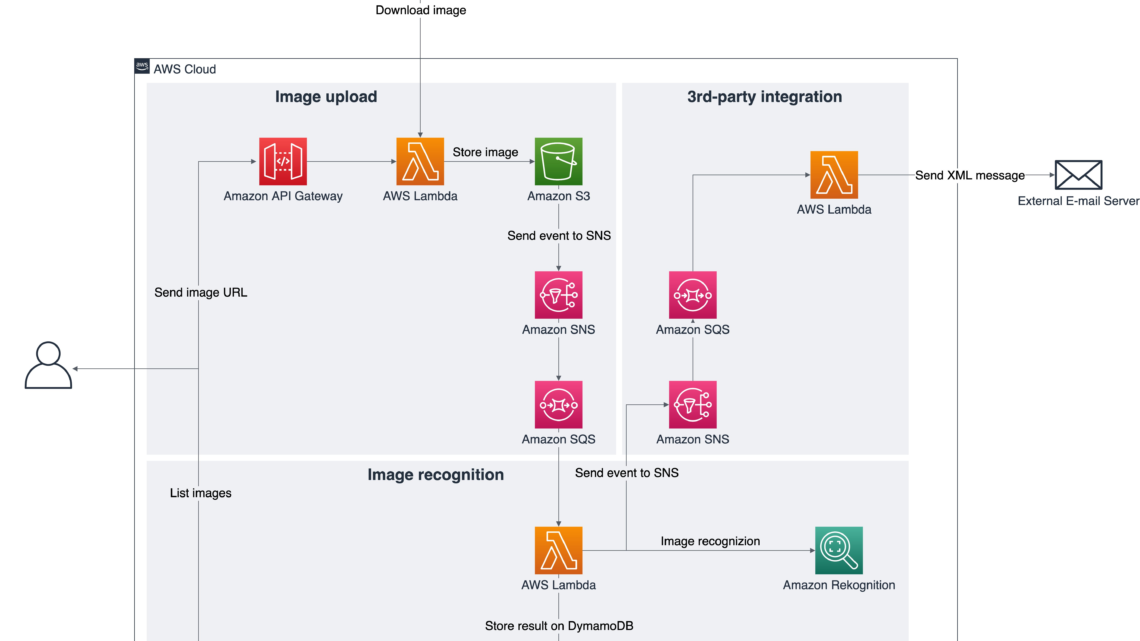
The following diagram depicts the architecture of our application:

Figure 1. Architecture diagram depicting the application architecture. It contains the service icons with the component explained on the text above.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, you must have the following prerequisites:
- An AWS account and an Administrator user
- Install and authenticate the AWS CLI. You can authenticate with an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) user or an AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) token.
- Install Python 3.7 or later.
- Install Node Package Manager (npm).
- Install the AWS CDK Toolkit.
- Install the AWS Toolkit for VS Code or for JetBrains.
- Install Git.
Configure environment
We already created the scaffolding for the application that we’ll build, which you can find on this Git repository. This application is represented by a CDK app that describes the infrastructure according to the architecture diagram above. However, the actual business logic of the application isn’t provided. You’ll implement it using CodeWhisperer. This means that we already declared using AWS CDK components, such as the API Gateway endpoints, DynamoDB table, and topics and queues. If you’re new to AWS CDK, then we encourage you to go through the CDK workshop later on.
Deploying AWS CDK apps into an AWS environment (a combination of an AWS account and region) requires that you provision resources that the AWS CDK needs to perform the deployment. These resources include an Amazon S3 bucket for storing files and IAM roles that grant permissions needed to perform deployments. The process of provisioning these initial resources is called bootstrapping. The required resources are defined in an AWS CloudFormation stack, called the bootstrap stack, which is usually named CDKToolkit. Like any CloudFormation stack, it appears in the CloudFormation console once it has been deployed.
After cloning the repository, let’s deploy the application (still without the business logic, which we’ll implement later on using CodeWhisperer). For this post, we’ll implement the application in Python. Therefore, make sure that you’re under the python directory. Then, use the cdk bootstrap command to bootstrap an AWS environment for AWS CDK. Replace {AWS_ACCOUNT_ID} and {AWS_REGION} with corresponding values first:
For more information about bootstrapping, refer to the documentation.
The last step to prepare your environment is to enable CodeWhisperer on your IDE. See Setting up CodeWhisperer for VS Code or Setting up Amazon CodeWhisperer for JetBrains to learn how to do that, depending on which IDE you’re using.
Image download
Let’s get started by implementing the first Lambda function, which is responsible for downloading an image from the provided URL and storing that image in an S3 bucket. Open the get_save_image.py file from the python/api/runtime/ directory. This file contains an empty Lambda function handler and the needed inputs parameters to integrate this Lambda function.
urlis the URL of the input image provided by the user,nameis the name of the image provided by the user, andS3_BUCKETis the S3 bucket name defined by our application infrastructure.
Write a comment in natural language that describes the required functionality, for example:
To trigger CodeWhisperer, hit the Enter key after entering the comment and wait for a code suggestion. If you want to manually trigger CodeWhisperer, then you can hit Option + C on MacOS or Alt + C on Windows. You can browse through multiple suggestions (if available) with the arrow keys. Accept a code suggestion by pressing Tab. Discard a suggestion by pressing Esc or typing a character.
For more information on how to work with CodeWhisperer, see Working with CodeWhisperer in VS Code or Working with Amazon CodeWhisperer from JetBrains.
You should get a suggested implementation of a function that downloads a file using a specified URL. The following image shows an example of the code snippet that CodeWhisperer suggests:

Figure 2. Screenshot of the code generated by CodeWhisperer on VS Code. It has a function called get_file_from_url with the implementation suggestion to download a file using the requests lib.
Be aware that CodeWhisperer uses artificial intelligence (AI) to provide code recommendations, and that this is non-deterministic. The result you get in your IDE may be different from the one on the image above. If needed, fine-tune the code, as CodeWhisperer generates the core logic, but you might want to customize the details depending on your requirements.
Let’s try another action, this time to upload the image to an S3 bucket:
As a result, CodeWhisperer generates a code snippet similar to the following one:

Figure 3. Screenshot of the code generated by CodeWhisperer on VS Code. It has a function called upload_image with the implementation suggestion to download a file using the requests lib and upload it to S3 using the S3 client.
Now that you have the functions with the functionalities to download an image from the web and upload it to an S3 bucket, you can wire up both functions in the Lambda handler function by calling each function with the correct inputs.
Image recognition
Now let’s implement the Lambda function responsible for sending the image to Amazon Rekognition for processing, storing the results in a DynamoDB table, and sending a message with those results as JSON to a second Amazon SNS topic. Open the image_recognition.py file from the python/recognition/runtime/ directory. This file contains an empty Lambda and the needed inputs parameters to integrate this Lambda function.
queue_urlis the URL of the Amazon SQS queue to which this Lambda function is subscribed,table_nameis the name of the DynamoDB table, andtopic_arnis the ARN of the Amazon SNS topic to which this Lambda function is published.
Using CodeWhisperer, implement the business logic of the next Lambda function as you did in the previous section. For example, to detect the labels from an image using Amazon Rekognition, write the following comment:
And as a result, CodeWhisperer should give you a code snippet similar to the one in the following image:

Figure 4. Screenshot of the code generated by CodeWhisperer on VS Code. It has a function called detect_labels with the implementation suggestion to use the Rekognition SDK to detect labels on the given image.
You can continue generating the other functions that you need to fully implement the business logic of your Lambda function. Here are some examples that you can use:
Following the same approach, open the list_images.py file from the python/recognition/runtime/ directory to implement the logic to list all of the labels from the DynamoDB table. As you did previously, type a comment in plain English:
Other frequently used code
Interacting with AWS isn’t the only way that you can leverage CodeWhisperer. You can use it to implement repetitive tasks, such as creating unit tests and converting message formats, or to implement algorithms like sorting and string matching and parsing. The last Lambda function that we’ll implement as part of this post is to convert a JSON payload received from Amazon SQS to XML. Then, we’ll POST this XML to an HTTP endpoint.
Open the send_email.py file from the python/integration/runtime/ directory. This file contains an empty Lambda function handler. An event is a JSON-formatted document that contains data for a Lambda function to process. Type a comment with your intent to get the code snippet:
As CodeWhisperer uses the context of your files to generate code, depending on the imports that you have on your file, you’ll get an implementation such as the one in the following image:

Figure 5. Screenshot of the code generated by CodeWhisperer on VS Code. It has a function called json_to_xml with the implementation suggestion to transform JSON payload into XML payload.
Repeat the same process with a comment such as # Send XML string with HTTP POST to get the last function implementation. Note that the email server isn’t part of this implementation. You can mock it, or simply ignore this HTTP POST step. Lastly, wire up both functions in the Lambda handler function by calling each function with the correct inputs.
Deploy and test the application
To deploy the application, run the command cdk deploy --all. You should get a confirmation message, and after a few minutes your application will be up and running on your AWS account. As outputs, the APIStack and RekognitionStack will print the API Gateway endpoint URLs. It will look similar to this example:
- The first endpoint expects two string parameters:
url(the image file URL to download) andname(the target file name that will be stored on the S3 bucket). Use any image URL you like, but remember that you must encode an image URL before passing it as a query string parameter to escape the special characters. Use an online URL encoder of your choice for that. Then, use thecurlcommand to invoke the API Gateway endpoint:
Replace {encoded-image-URL} and {file-name} with the corresponding values. Also, make sure that you use the correct API endpoint that you’ve noted from the AWS CDK deploy command output as mentioned above.
- It will take a few seconds for the processing to happen in the background. Once it’s ready, see what has been stored in the DynamoDB table by invoking the List Images API (make sure that you use the correct URL from the output of your deployed AWS CDK stack):
After you’re done, to avoid unexpected charges to your account, make sure that you clean up your AWS CDK stacks. Use the cdk destroy command to delete the stacks.
Conclusion
In this post, we’ve seen how to get a significant productivity boost with the help of ML. With that, as a developer, you can stay focused on your IDE and reduce the time that you spend searching online for code snippets that are relevant for your use case. Writing comments in natural language, you get context-based snippets to implement full-fledged applications. In addition, CodeWhisperer comes with a mechanism called reference tracker, which detects whether a code recommendation might be similar to particular CodeWhisperer training data. The reference tracker lets you easily find and review that reference code and see how it’s used in the context of another project. Lastly, CodeWhisperer provides the ability to run scans on your code (generated by CodeWhisperer as well as written by you) to detect security vulnerabilities.
During the preview period, CodeWhisperer is available to all developers across the world for free. Get started with the free preview on JetBrains, VS Code or AWS Cloud9.
About the author:
